For 반복구문 (리스트와 행렬 예제 포함)
for 반복구문은 우리가 요소의 목록이나 숫자의 범위를 반복해야 할 때 매우 유용하다. 반복구문(loop)은 리스트, 데이터 프레임, 벡터, 행렬 또는 다른 객체를 반복하는 데 사용할 수 있다. 중괄호({})와 대괄호([])는 필수적이다.
이번 튜토리얼에서는 다음의 내용을 학습힌다 :
For 반복구문의 표기법과 예제
xxxxxxxxxxFor (i in vector) {Exp}
여기에서,
R은 벡터 내에 있는 모든 변수들에 대해 반복할 것이며 Exp 내에 작성된 연산을 수행할 것이다.
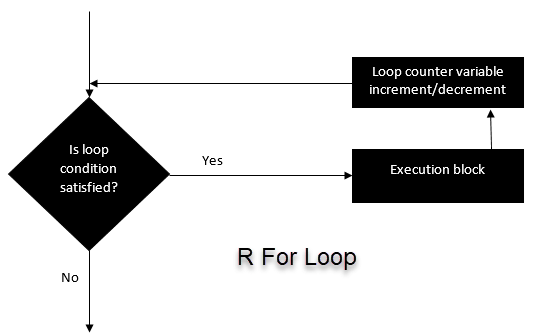
몇 개의 예를 살펴보자.
예제 1 : 우리는 벡터의 모든 요소에 대해 반복하여 그 현재 값을 출력한다.
xxxxxxxxxx# Create fruit vectorfruit <- c('Apple', 'Orange', 'Passion fruit', 'Banana')# Create the for statementfor ( i in fruit){print(i)}
결과 :
xxxxxxxxxx## [1] "Apple"## [1] "Orange"## [1] "Passion fruit"## [1] "Banana"
예제 2 : 1부터 4 사이의 x에 대한 다항식을 사용하여 비선형 함수를 생성하고 그것을 하나의 리스트에 저장해 보자.
xxxxxxxxxx# Create an empty listlist <- c()# Create a for statement to populate the listfor (i in seq(1, 4, by=1)) {list[[i]] <- i*i}print(list)
결과 :
xxxxxxxxxx## [1] 1 4 9 16
for 반복구문은는 기계 학습 작업에 매우 유용하다. 모델을 훈련한 후에, 모델이 과적합(over-fitting)하게 되지 않도록 모델을 정규화할 필요가 있다. 함수의 손실을 최소화하는 값을 찾아야 하기 때문에 정규화는 매우 지루한 작업이다. 이러한 값을 탐지할 수 있도록 for 반복구문을 사용하여 한 범위의 값들을 반복 수행하고 최적의 후보를 정의할 수 있다.
리스트에 대한 For 반복구문
리스트에 대한 반복처리는 벡터에 대한 반복처리 만큼이나 쉽고 편리하다. 다음의 예를 살펴보자.
xxxxxxxxxx# Create a list with three vectorsfruit <- list(Basket = c('Apple', 'Orange', 'Passion fruit', 'Banana'),Money = c(10, 12, 15), purchase = FALSE)for (p in fruit){print(p)}
결과 :
xxxxxxxxxx## [1] "Apple" "Orange" "Passion fruit" "Banana"## [1] 10 12 15## [1] FALSE
행렬에 대한 For 반복구문
행렬은 행과 열의 2차원으로 구성된다. 행렬에 대한 반복 수행을 위해 행에 대한 반복과 열에 대한 반복 등 2개의 for 반복구문을 정의해야 한다.
xxxxxxxxxx# Create a matrixmat <- matrix(data = seq(10, 20, by=1), nrow = 6, ncol =2)# Create the loop with r and c to iterate over the matrixfor (r in 1:nrow(mat))for (c in 1:ncol(mat))print(paste("Row", r, "and column",c, "have values of", mat[r,c]))
결과 :
xxxxxxxxxx## [1] "Row 1 and column 1 have values of 10"## [1] "Row 1 and column 2 have values of 16"## [1] "Row 2 and column 1 have values of 11"## [1] "Row 2 and column 2 have values of 17"## [1] "Row 3 and column 1 have values of 12"## [1] "Row 3 and column 2 have values of 18"## [1] "Row 4 and column 1 have values of 13"## [1] "Row 4 and column 2 have values of 19"## [1] "Row 5 and column 1 have values of 14"## [1] "Row 5 and column 2 have values of 20"## [1] "Row 6 and column 1 have values of 15"## [1] "Row 6 and column 2 have values of 10"