2.3 특수 그래프(Specific graphs)와 그래프 모델(graph models)
빈 그래프(Empty graph)
eg <- make_empty_graph(40)
plot(eg, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)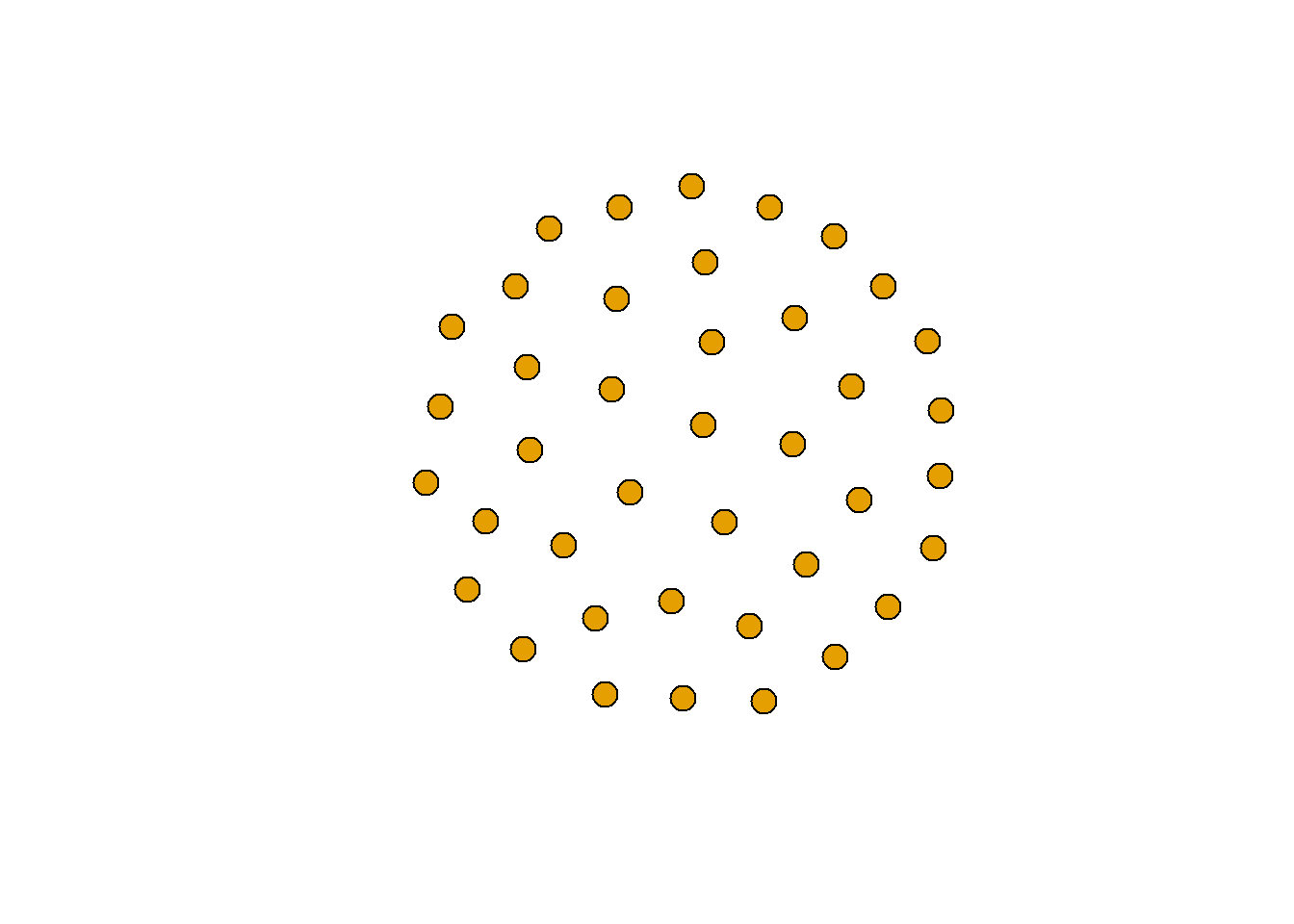
완전 그래프(Full graph)
fg <- make_full_graph(40)
plot(fg, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)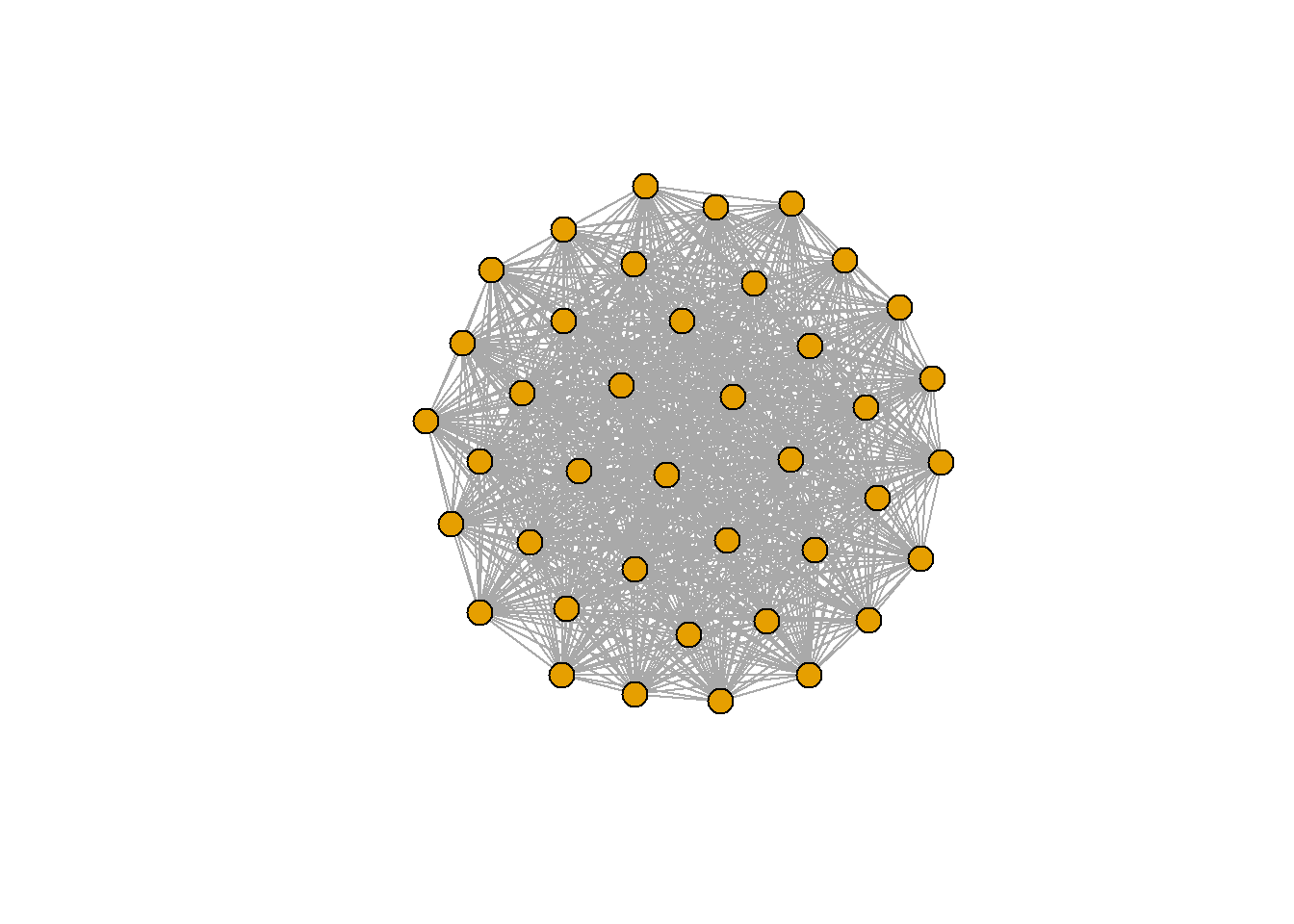
단순 성형 그래프(Simple star graph)
st <- make_star(40)
plot(st, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA) 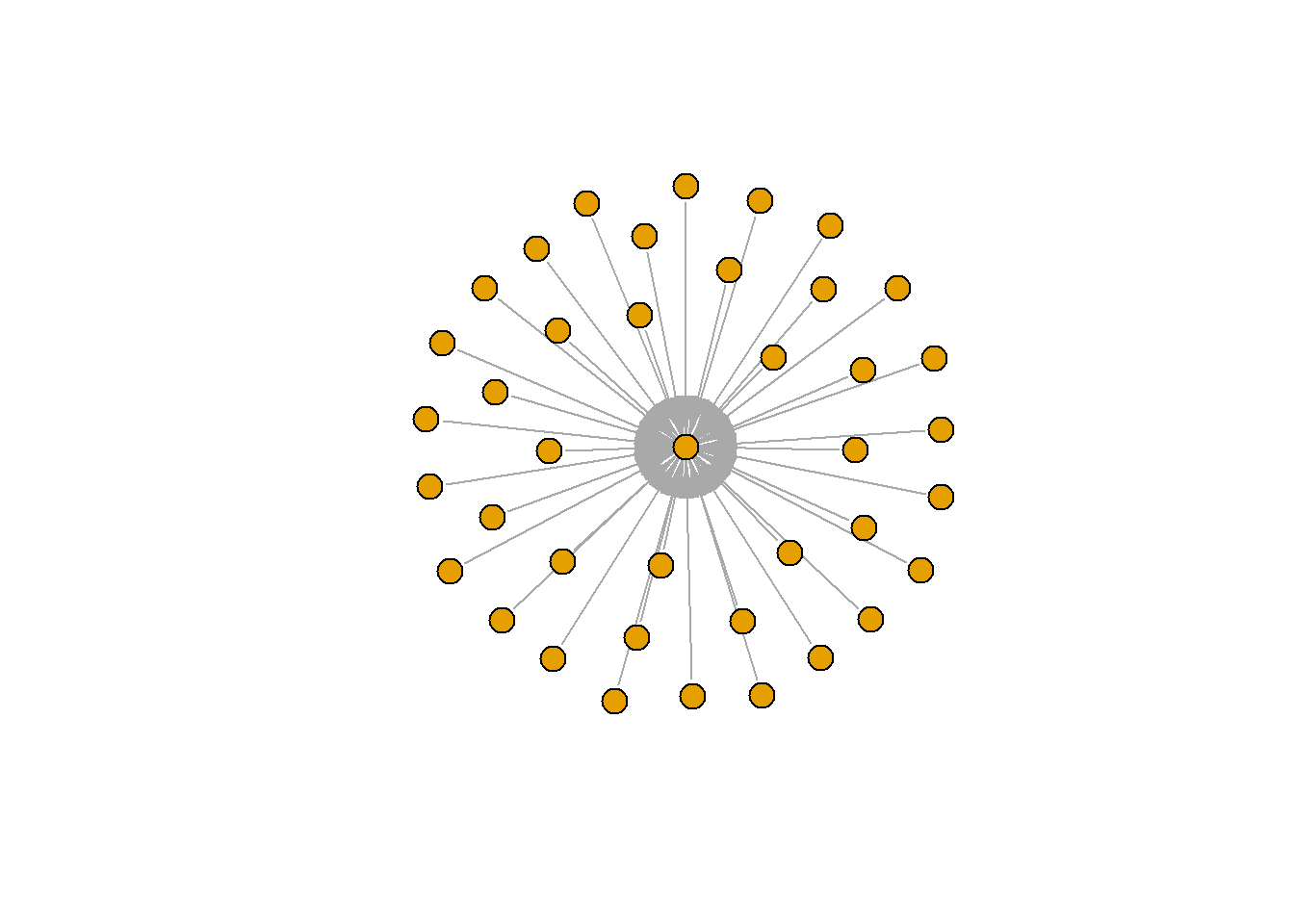
나무형 그래프(Tree graph)
tr <- make_tree(40, children = 3, mode = "undirected")
plot(tr, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA) 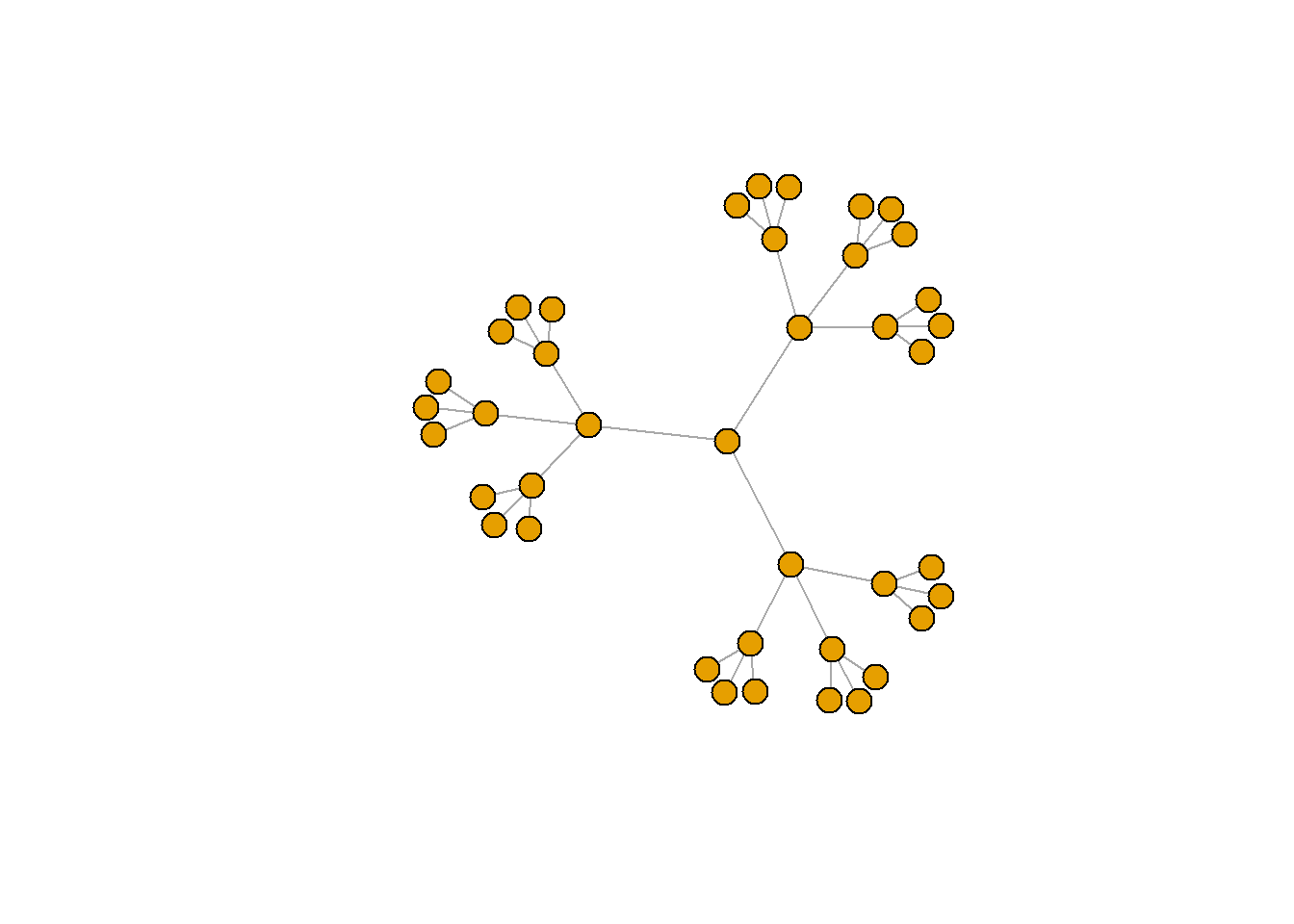
환형 그래프(Ring graph)
rn <- make_ring(40)
plot(rn, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)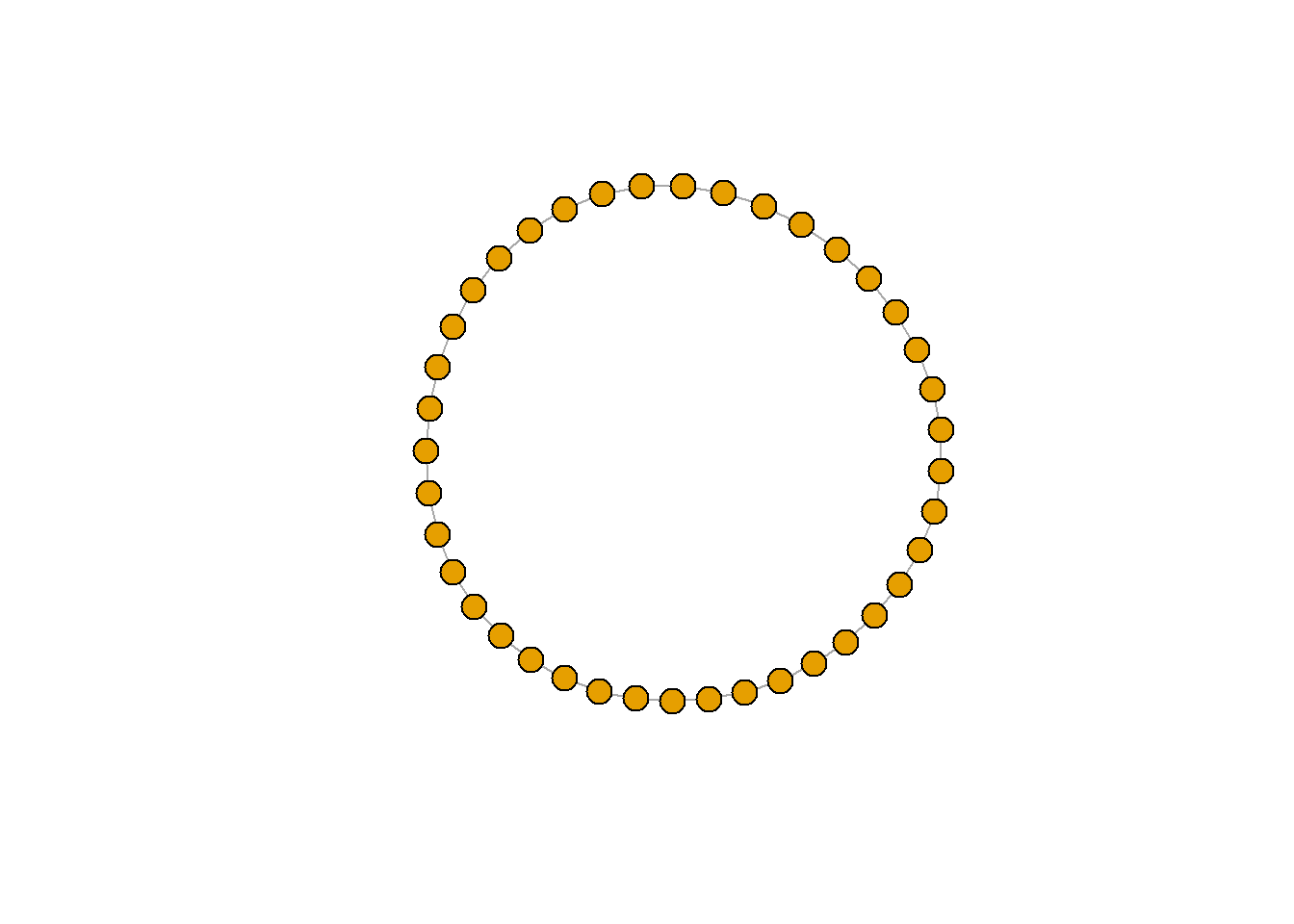
Erdos-Renyi random graph model
(‘n’ : 노드의 갯수, ‘m’ : 에지의 갯수).
[참고자료 : http://sanghyukchun.github.io/50/]
er <- sample_gnm(n=100, m=40)
plot(er, vertex.size=6, vertex.label=NA) 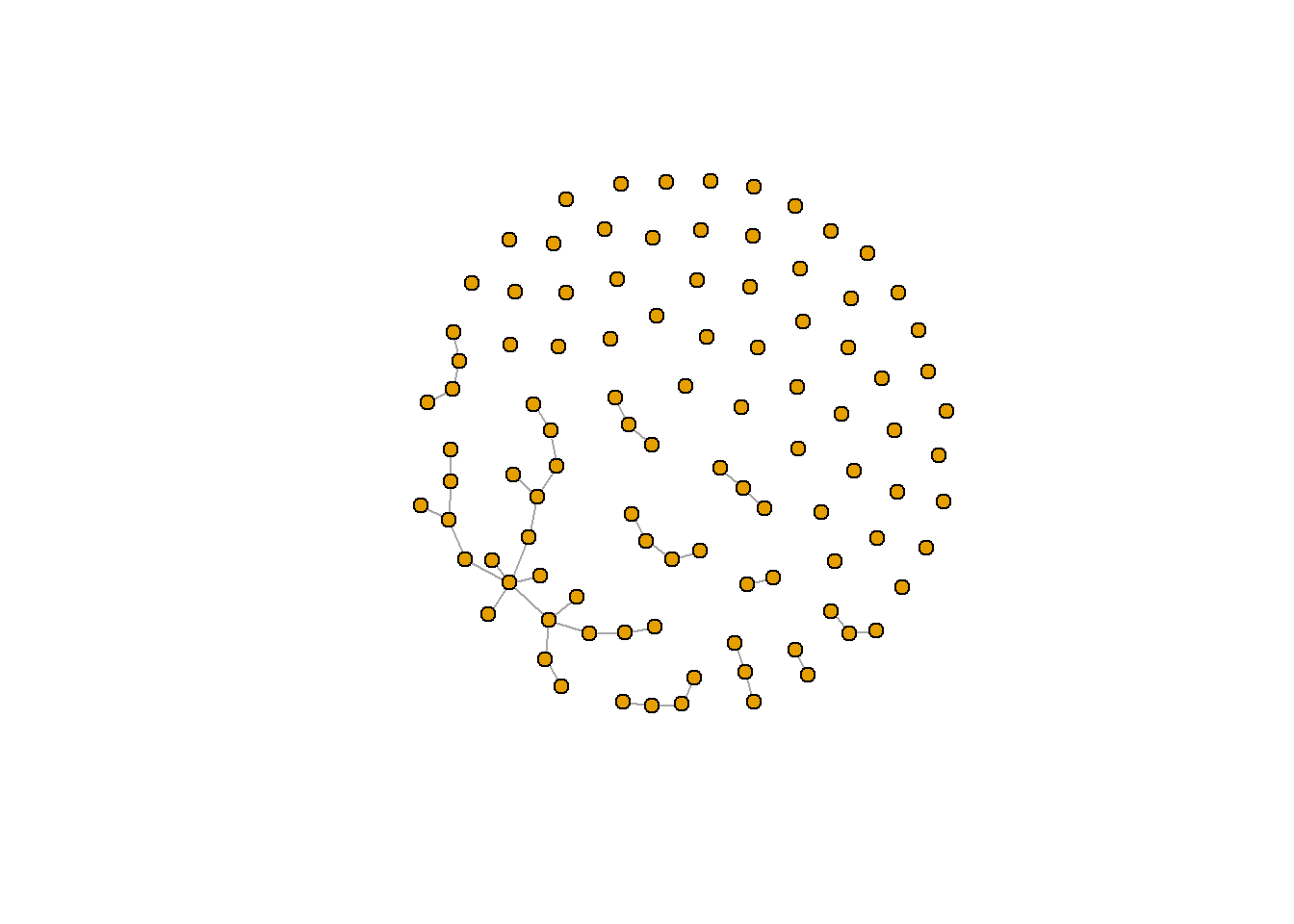
Watts-Strogatz small-world model
(dim 차원과 size 차원의 노드의 수를 갖는) lattice를 생성하고, 확률 p로 무작위로 에지를 연결한다.
에지가 연결된 이웃들은 nei이다. loops 와 다중(multiple) 에지를 허용할 수 있다.
[참고자료 : http://sanghyukchun.github.io/51/]
sw <- sample_smallworld(dim=2, size=10, nei=1, p=0.1)
plot(sw, vertex.size=6, vertex.label=NA, layout=layout_in_circle)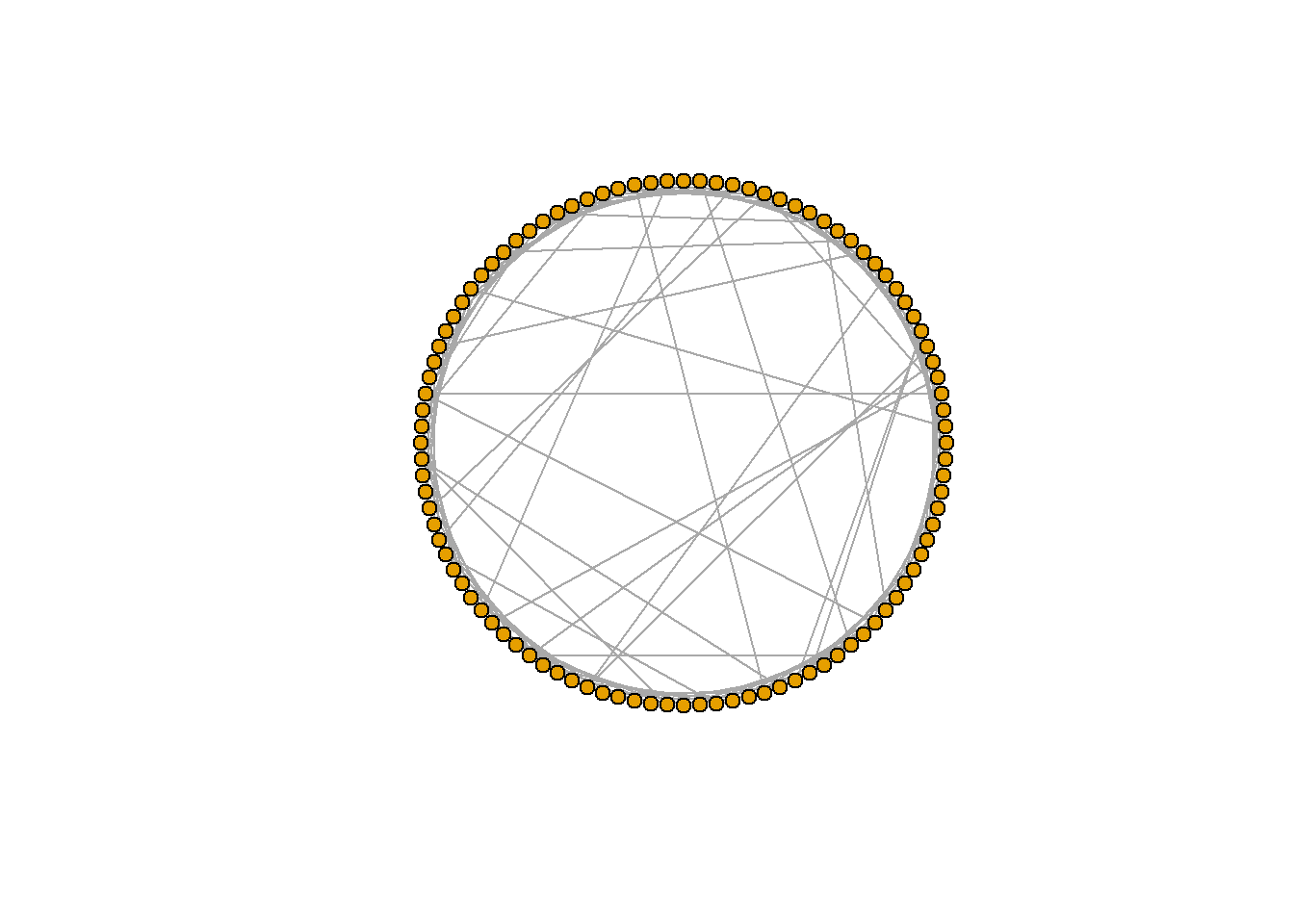
Barabasi-Albert preferential attachment model for scale-free graphs
(n : 노드의 갯수, power 제곱승 (1은 선형); m 각 시간 단계에 추가되는 에지의 갯수)
[참고자료 : http://sanghyukchun.github.io/52/]
ba <- sample_pa(n=100, power=1, m=1, directed=F)
plot(ba, vertex.size=6, vertex.label=NA)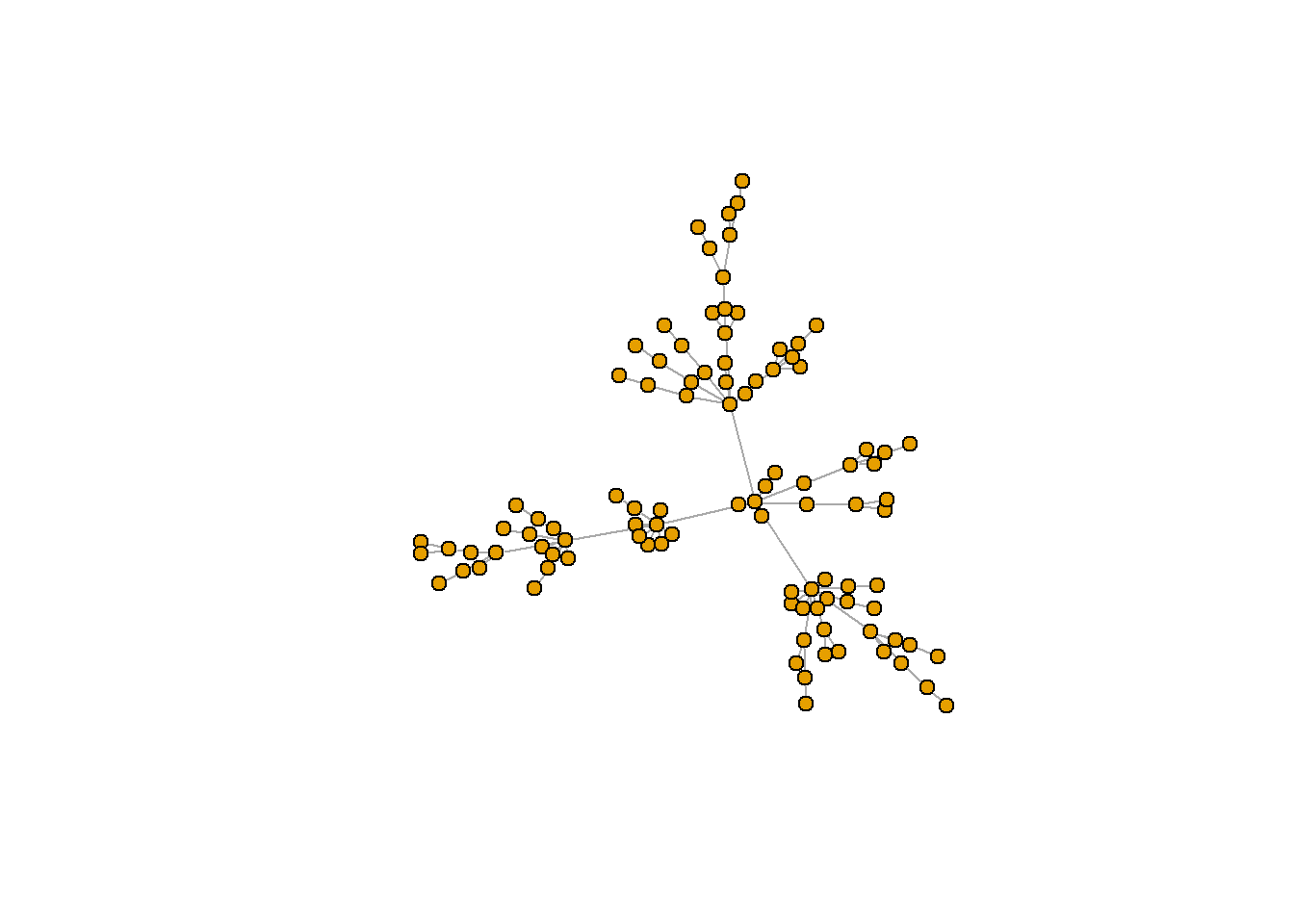
igraph 는 몇가지 주목할 만한 역사적인 그래프를 제공할 수 있다. 예를 들어,
zach <- graph("Zachary") # the Zachary carate club
plot(zach, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)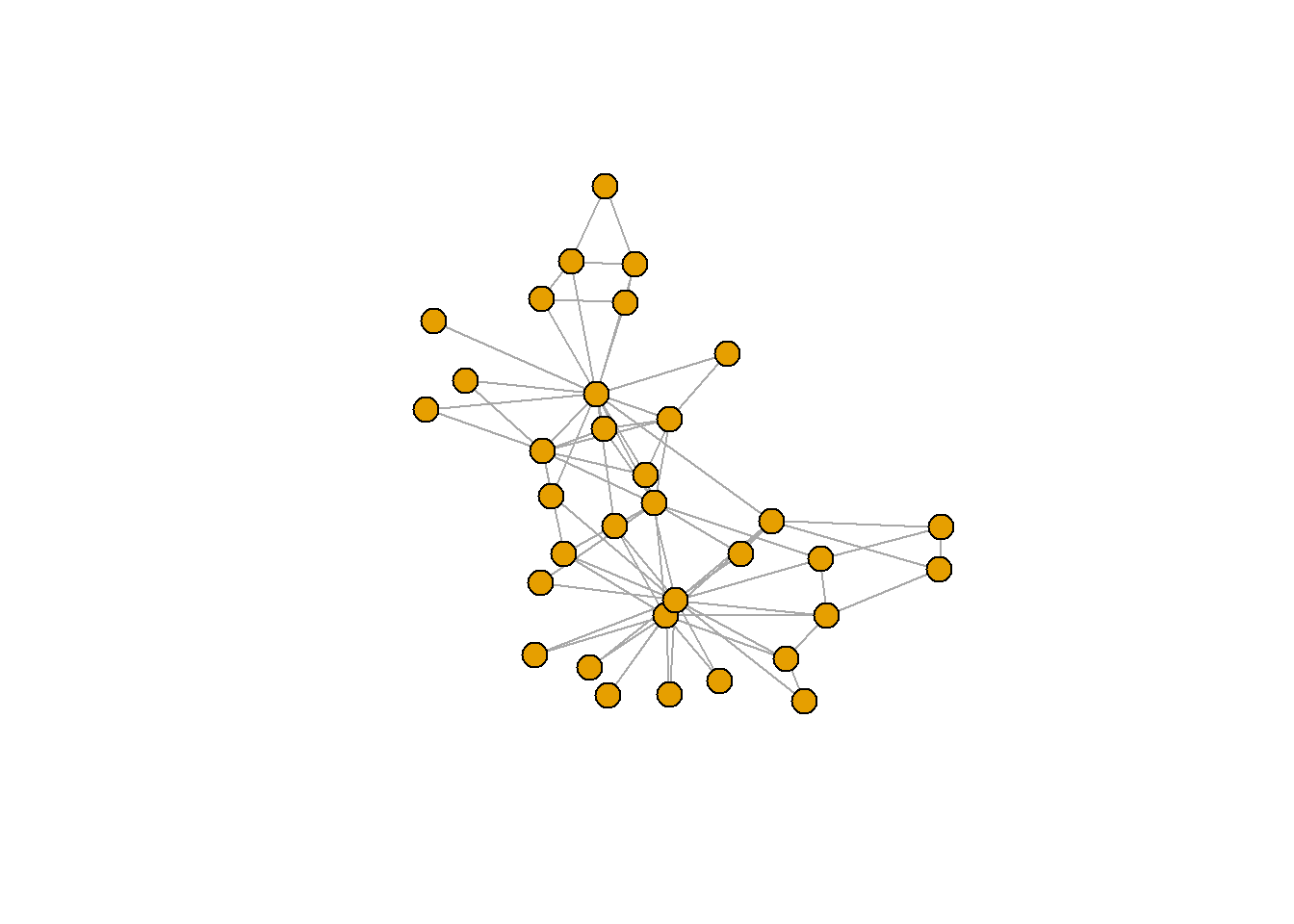
Rewiring a graph
each_edge() 은 확률 prob으로 일양분포하는 에지의 끝단을 변경하는 재연결 방법이다.
rn.rewired <- rewire(rn, each_edge(prob=0.1))
plot(rn.rewired, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)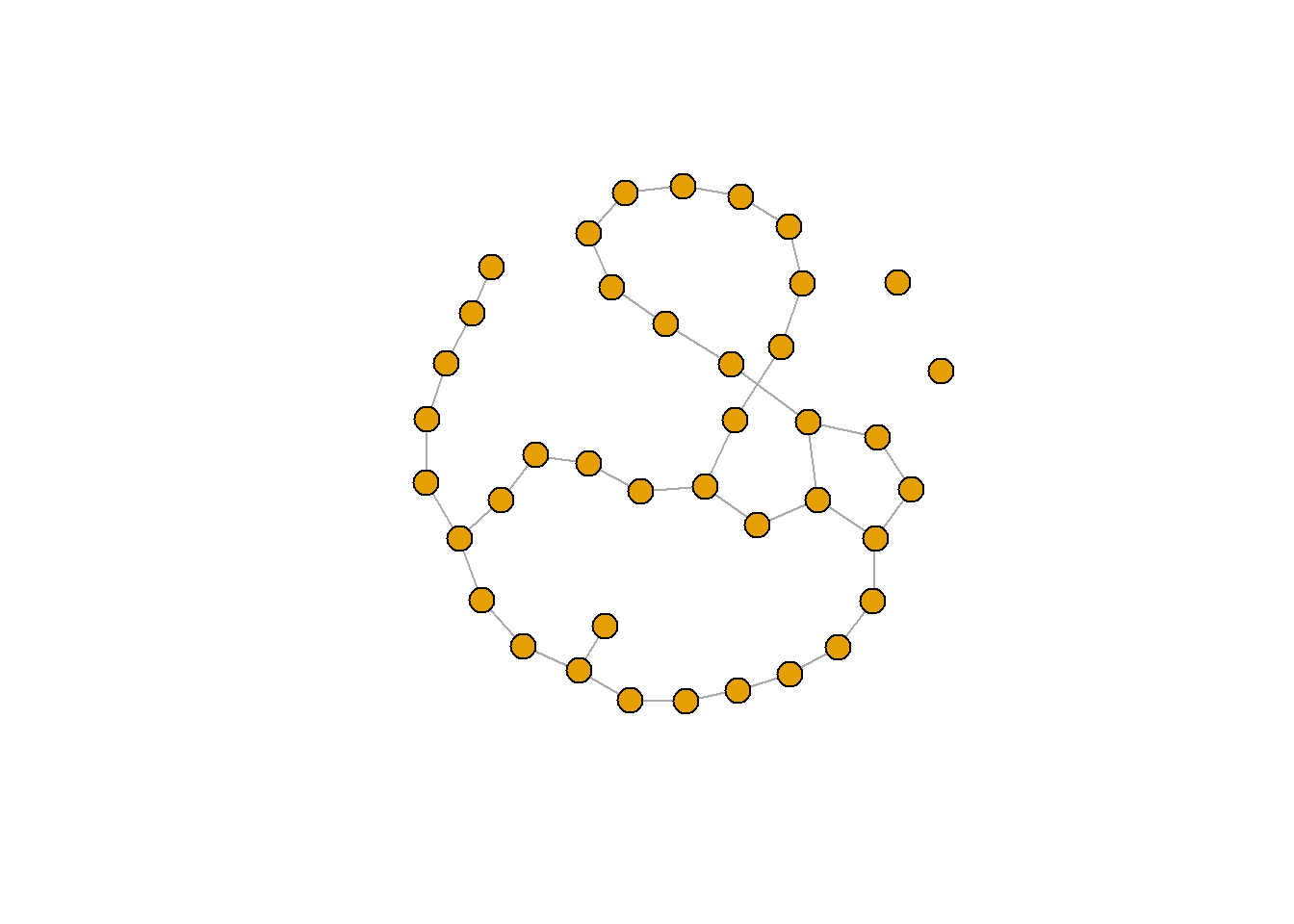
특정 거리에서 정점들을 다른 정점들과 연결하기 위한 리와이어.
rn.neigh = connect.neighborhood(rn, 5)
plot(rn.neigh, vertex.size=8, vertex.label=NA) 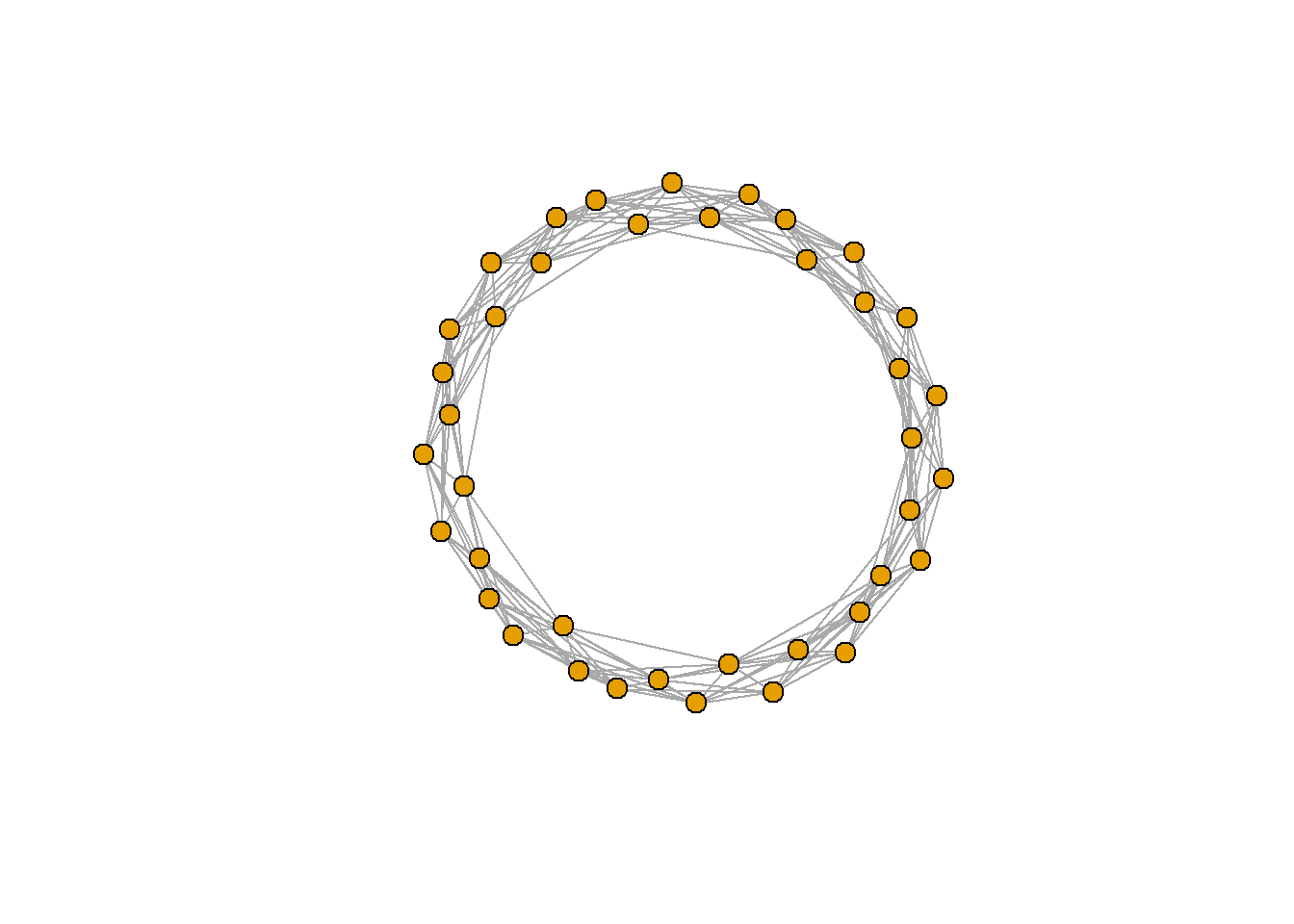
그래프의 결합(분리된 정점 집합을 가정한 상호배제 합집합(disjoint union) ) : %du%
plot(rn, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)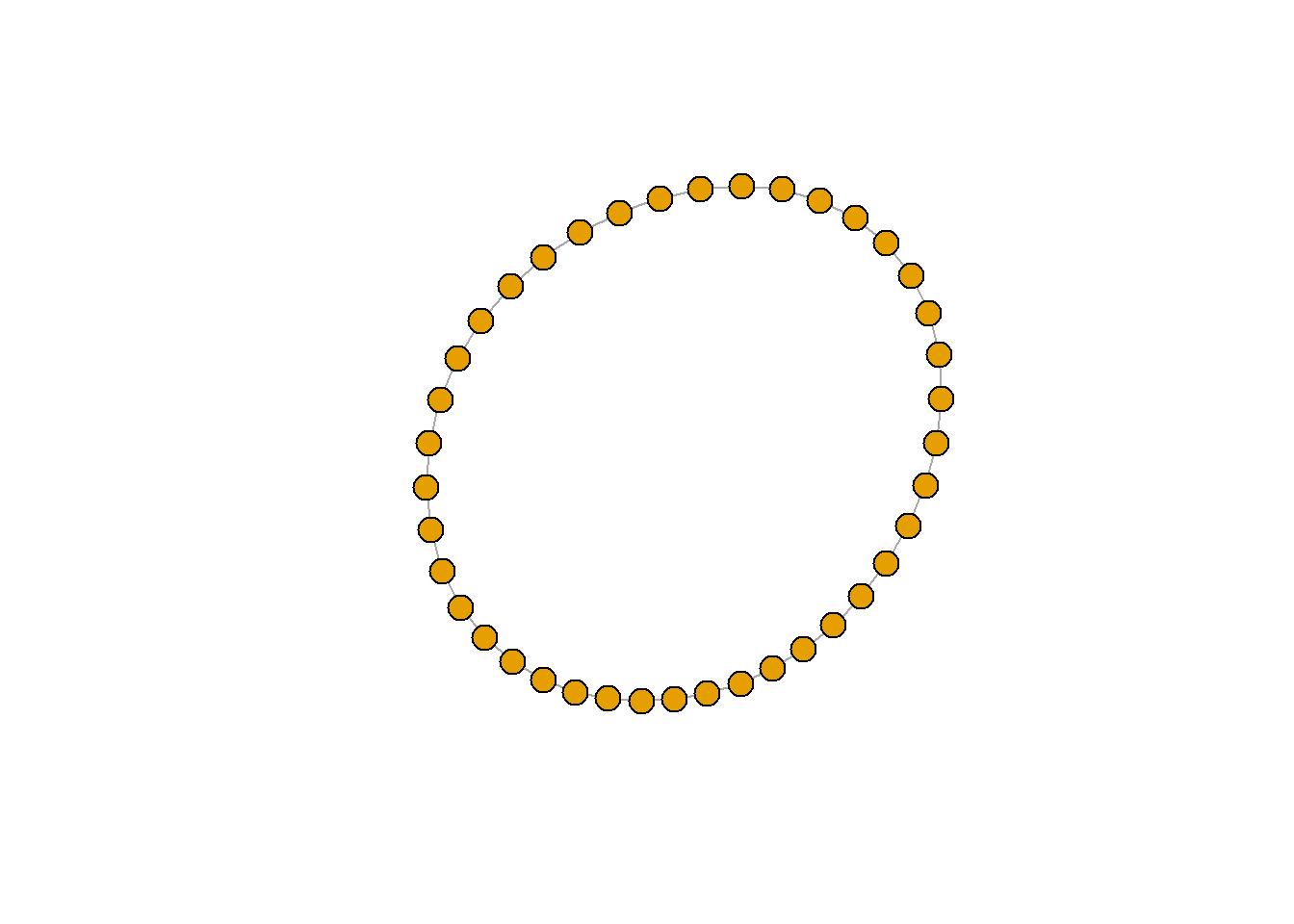
plot(tr, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)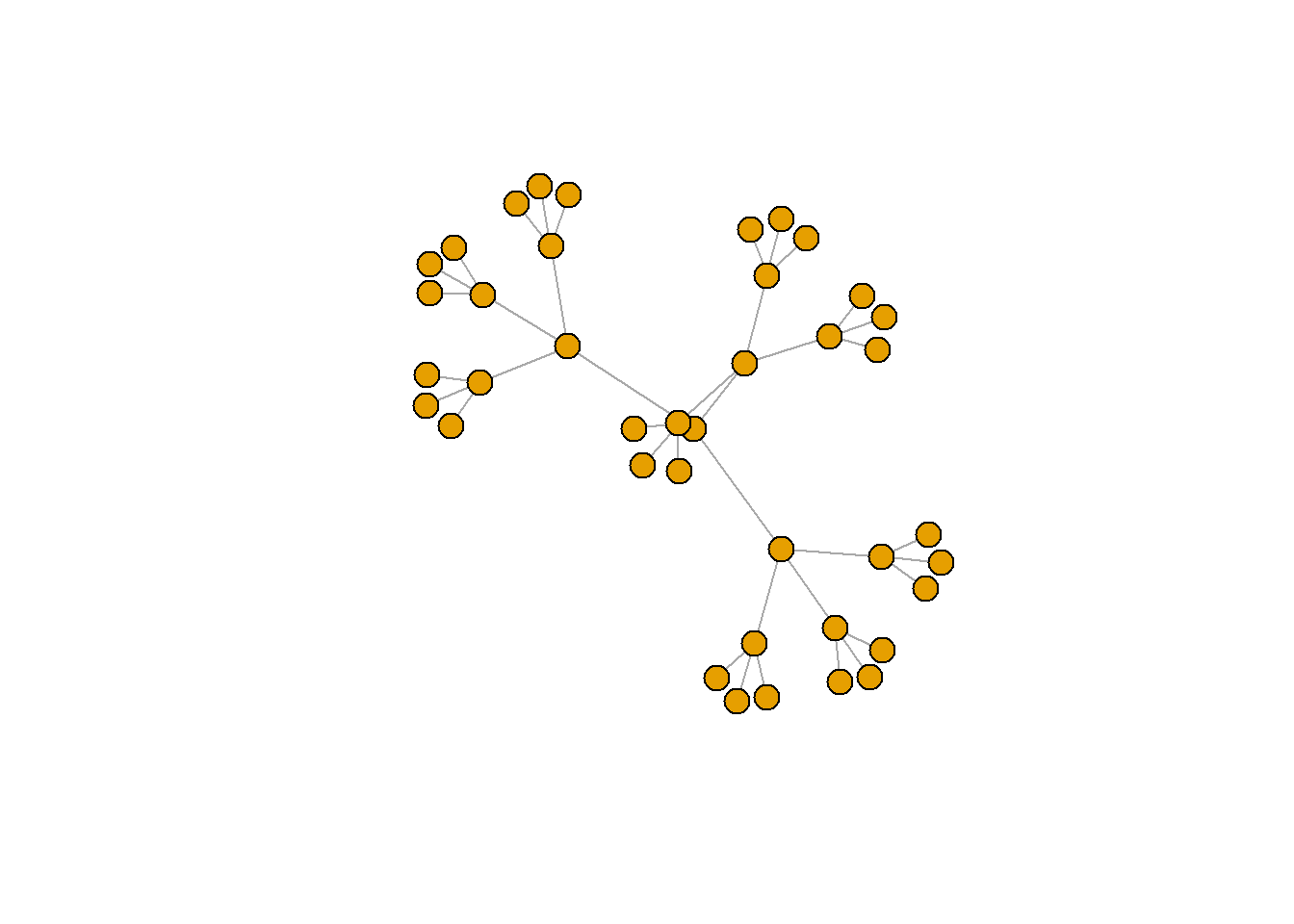
plot(rn %du% tr, vertex.size=10, vertex.label=NA)